Husky A300 Integration

CAUTION
Always perform a risk assessment prior to any custom integrations.
Custom integrations are outside the scope of the base robot's safety assessment and custom integrations may result in new hazards.
To attach custom hardware to Husky, you will have to take care of mechanical mounting, electrical supply, and software integration. This guide aims to equip you with respect to these challenges.
Mechanical Mounting
Husky A300 is equipped with a PACS™ top plate for mounting additional sensors and equipment.
PACS™ Mounting and Kits
PACS™ is a Clearpath Robotics standard, providing a grid of M5X0.8 holes onto the top plate of the robot. This grid of holes has a 80 mm X 80 mm spacing. You can create your own brackets to interface with these holes, or can use an existing Clearpath Robotics bracket.
Cable Passthrough
To maintain Husky's IP54 rating while allowing cables to pass between the external kits and internal electronics, Husky's top plate is provisioned with expansion plates for cable IP-rated cable systems. There are three expansion plates at the front and three at the rear of the top plate.
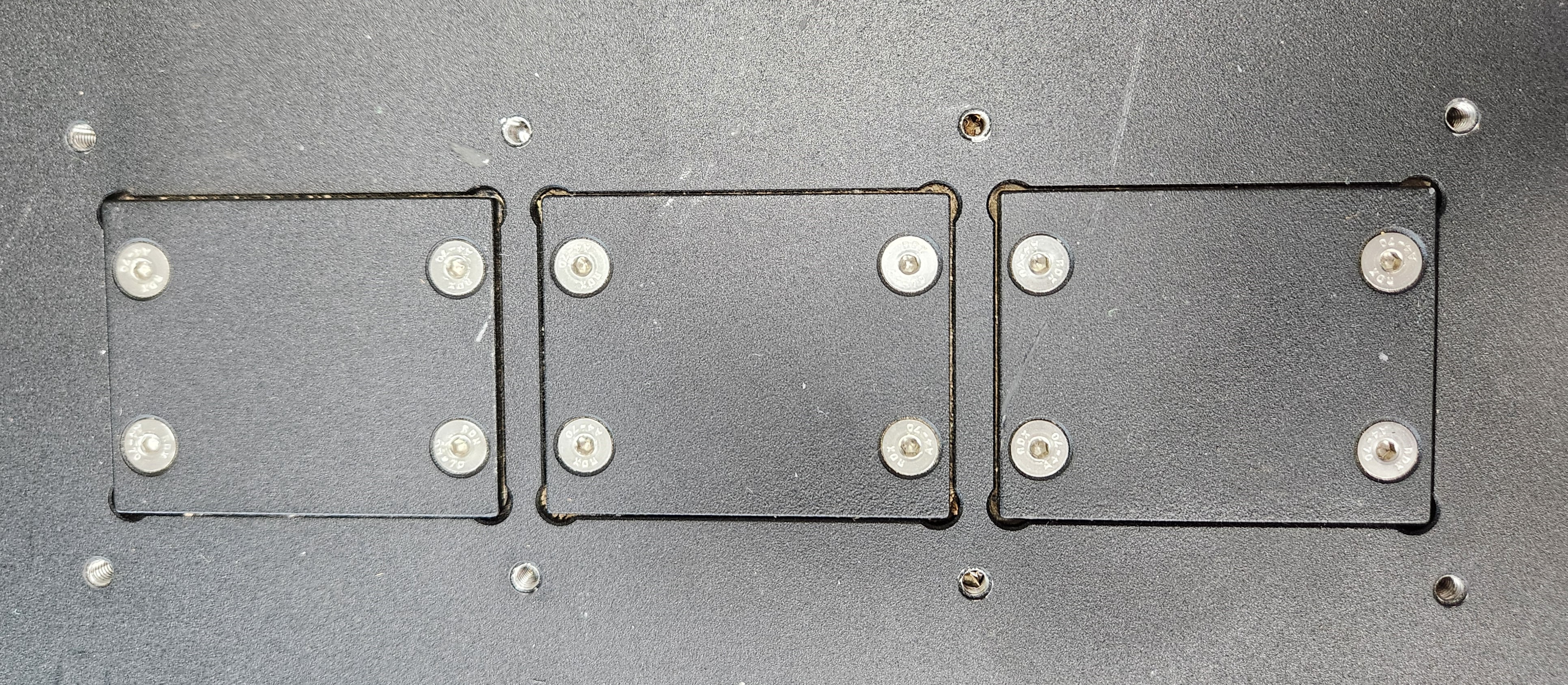
Users have two main options.
- Drill holes in the expansion plates and add appropriate IP-rated sealing solutions on a cable-by-cable basis.
- Remove an expansion plate and replace it with a cable entry system, such as Icotek, which is described in more detail below.
Using the Icotek Cable Entry System
The Icotek Cable Entry System allows pre-terminated cables up to 65 mm in diameter to be routed into Husky A300 and be sealed with up to IP66 rated ingress protection (certified according to EN 60529 / UL50-E). In addition, the cable entry frames serve as strain relief on the cable (based on EN 62444).
This cable system is based on a set of cable entry frames and grommets. Refer to the demonstration video for an overview of using the system.
Supported cable entry frames are listed in the table below.
| Part Number | Part Description | CPR Item Number | Retailer Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| KEL-ER-B4 V2A (48204.200) | IP66 2X2 cable entry frame | 031682 | RS-Online |
| Gasket B (42452) | Gasket for KEL-ER-B4 | 031350 | RS-Online |
| KEL-FG-ER-E2 (42345) | IP65 1X2 cable entry frame, 90° | 032777 | RS-Online |
| Gasket E2 (42256) | Gasket for KEL-FG-ER-E2 | 032788 | Contact Icotek for local supplier |
| DB 3X1 | M32 (54300) | Cable Gland Enclosure, 1X3 Small, 360⁰ | 028997 |
Grommets are selected based on the size of the cable being passed through. A list of the most common grommets are listed in the table below. See also full grommets product catalog.
| Part Number | Part Description | CPR Item Number | Retailer Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank BK (41351) | Blank grommet | 031393 | RS-Online |
| KT 1 BK (39943) | 1X Split grommet for 1-2 mm cable | N/A | RS-Online |
| KT 2 BK (41302) | 1X Split grommet for 2-3 mm cable | 032027 | RS-Online |
| KT 3 BK (41303) | 1X Split grommet for 3-4 mm cable | N/A | RS-Online |
| KT 4 BK (41304) | 1X Split grommet for 4-5 mm cable | 032536 | RS-Online |
| KT 5 BK (41305) | 1X Split grommet for 5-6 mm cable | N/A | RS-Online |
| KT 6 BK (41306) | 1X Split grommet for 6-7 mm cable | 031394 | RS-Online |
| KT 7 BK (41307) | 1X Split grommet for 7-8 mm cable | N/A | RS-Online |
| KT 8 BK (41308) | 1X Split grommet for 8-9 mm cable | N/A | RS-Online |
| KT 9 BK (41309) | 1X Split grommet for 9-10 mm cable | 031395 | RS-Online |
| KT 10 BK (41310) | 1X Split grommet for 10-11 mm cable | 032535 | RS-Online |
| KT 11 BK (41311) | 1X Split grommet for 11-12 mm cable | 031396 | RS-Online |
| KT 2/6 BK (39905) | 2X Split grommet for 6-7 mm cable | 028994 | RS-Online |
| KT 2/7 BK (39916) | 2X Split grommet for 7-8 mm cable | 031398 | RS-Online |
| KT 2/8 BK (39918) | 2X Split grommet for 8-9 mm cable | 032028 | RS-Online |
| KT 4/5 BK (39910) | 4X Split grommet for 5-6 mm cable | 031399 | RS-Online |
| KT 4/6 BK (39933) | 4X Split grommet for 6-7 mm cable | 031400 | RS-Online |
Electrical Integration
Except for bus-powered USB cameras, most payloads have separate leads for power and data. Some payloads also make use of signalling through the AUX inputs and outputs on the Main circuit board or through the Digital I/O pins on the computer.
Refer to Cable Passthrough for details on how to pass cables through Husky's top plate for external payloads.
Data Connections
Data connections (USB and Ethernet) are made to the Husky computer mounted inside the chassis. These may be direct connections to the computer where ports are available or through USB hubs and network switches where expansion is required.
Main Circuit Board Connector Summary
The Main circuit board provides a number of connections for power, fans, relays, GPIOs, auxiliary inputs and auxiliary outputs. These are summarized in the following table and described in more detail in the following sections.
| MCU board label | MCU board connector | Mating connector | Crimp terminals | Crimping tool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USER 1 - USER 8 | Molex 0039296088 | Molex 0039012080 | Molex 0039000140 (AWG 22-28) or Molex 0039000073 (AWG 18-24) | Molex 0638191000 |
| EXP 1 - EXP 2 | Molex 1720650202 | Molex 1700010102 | Molex 1720630311 (AWG 14-16) or Molex 1720630312 (AWG 12) | Molex 2238631200 |
| EXP CTRL | TE 3-794682-8 | TE 794617-8 | TE 1-794606-1 (AWG 20-24) or TE 1-794607-1 (AWG 26-30) | TE 91391-1 |
| AUX1 IN, AUX2 IN, AUX3 IN | TE 3-794682-6 | TE 794617-6 | TE 1-794606-1 (AWG 20-24) or TE 1-794607-1 (AWG 26-30) | TE 91391-1 |
| AUX1 OUT, AUX2 OUT, AUX3 OUT | TE 3-794682-8 | TE 794617-8 | TE 1-794606-1 (AWG 20-24) or TE 1-794607-1 (AWG 26-30) | TE 91391-1 |
| GPIO | TE 4-794680-6 | TE 1-794617-6 | TE 1-794606-1 (AWG 20-24) or TE 1-794607-1 (AWG 26-30) | TE 91391-1 |
| FAN 5 - FAN 8 | Molex 0705430003 | Molex 0050579404 | Molex 0016020103 (AWG 22-24) | Molex 0638118700 |
| W ES (Wireless E-Stop) | TE 4-794682-0 | TE 1-794617-0 | TE 1-794606-1 (AWG 20-24) or TE 1-794607-1 (AWG 26-30) | TE 91391-1 |
| ES 3 - ES 8 (E-Stop) | TE 3-794682-4 | TE 794617-4 | TE 1-794606-1 (AWG 20-24) or TE 1-794607-1 (AWG 26-30) | TE 91391-1 |
| SYS1 - SYS 2 | Molex 1720650204 | Molex 1700010104 | Molex 1720630311 (AWG 14-16) or Molex 1720630312 (AWG 12) | Molex 2238631200 |
| SYS3 | Molex 1720650206 | Molex 1700010106 | Molex 1720630311 (AWG 14-16) or Molex 1720630312 (AWG 12) | Molex 2238631200 |
| SYS4 | Molex 0039281023 | Molex 0039012020 | Molex 0039000140 (AWG 22-28) or Molex 0039000073 (AWG 18-24) | Molex 0638191000 |
Power Connections
User Power Connections
The Main circuit board provides eight connectors, labelled USER 1 through USER 8, for user power.
User power is divided into four power rails and the power for each rail is shared across each of the 8 connectors. The maximum (aggregate) current available on each power rail is outlined in the table below.
| User Power Rail | Maximum (Aggregate) Current |
|---|---|
| 12 V Rail A | 5 A |
| 12 V Rail B | 5 A |
| 24 V | 5 A |
| VBAT (24-29 V, unregulated) | 5 A |
WARNING
Do not exceed the specified maximum current limit of each power rail.
Failure to do so may result in damage to your payload.
User Power Pin Mapping
The pinout for each of the eight connectors (USER 1 - USER 8) is illustrated below.
| USER connector pin | Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | 12 V (Rail B) |
| 2 | 12 V (Rail A) |
| 3 | 24 V |
| 4 | VBAT (24-29 V, unregulated) |
| 5 | GND |
| 6 | GND |
| 7 | GND |
| 8 | GND |
Making Cables to Connect to User Power
Connecting to user power requires the use of a Molex connector and compatible crimp terminals. To create these cables, follow the steps below.
- Expose about 5 mm of bare wire from the payload power leads and twist the exposed wire on both leads.
- Take 2 Molex terminals from the spare parts kit provided and insert the exposed wire and crimp the terminals, ensuring the wires are well secured inside the terminal, as shown below.
- Take 1 connector housing from the spare parts kit provided and insert the positive payload power lead (red) into position 1, 2, 3 or 4 of the connector until it locks into place. The positions numbers are visible on the back of the plastic housing.
- Insert the negative payload power lead (black) into position 5, 6, 7, or 8 of the connector until it locks into place.

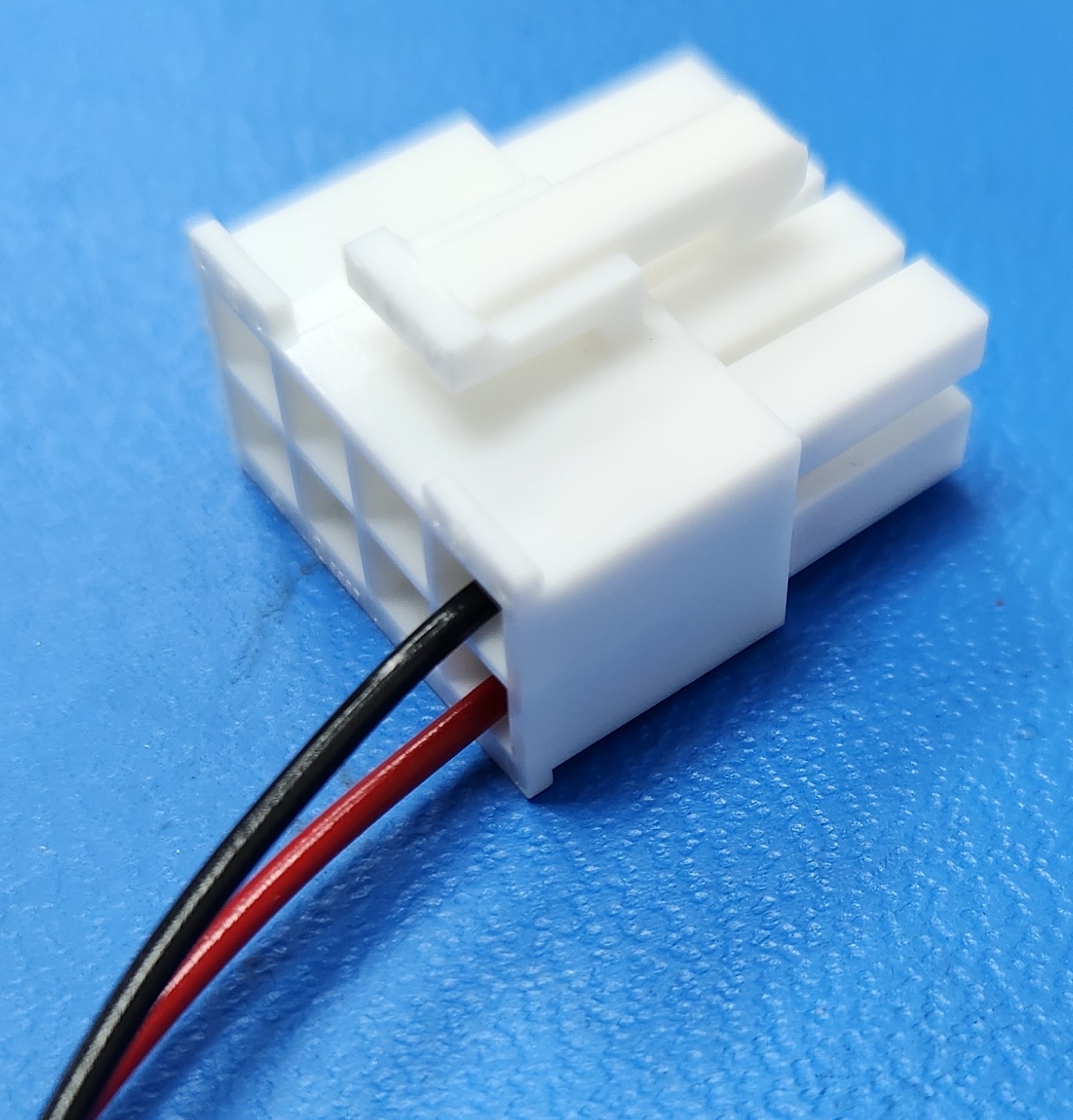
For more technical information on the Molex power connectors, as well as their corresponding mating connectors, please visit the Digi-Key WM3703-ND Product Page.
Software Control of User Power Rails
User power can be enabled or disabled through ROS by publishing to /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_user_power ROS topic.
To disable user power, run:
ros2 topic pub --once /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_user_power std_msgs/msg/Bool '{data: false}'
To enable user power, run:
ros2 topic pub --once /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_user_power std_msgs/msg/Bool '{data: true}'
User power is enabled by default shortly after the robot first powers up, regardless of its state when the robot was powered off.
High Power Expansion Kit
The optional High Power Expansion Kit can purchased at the time of your original Husky order, referring to CPR Item 032001. Field installation is not supported at present.
When using the optional High Power Expansion Kit while operating in environments with inclines of 5° (or more) AND with a payload of 50 kg (or more), a 4-battery or 6-battery configuration is recommended. Using a 2-battery configuration may provide insufficient power in the worst case. Contact Support for additional details.
Some high power payloads, such as manipulators, require more power than can be provided through the user power connectors. The optional High Power Expansion Kit provides access to VBAT at 40 A. It also includes two contactors for enabling and disabling power to the payload.
Creating a Mating Cable
To use the High Power Expansion Kit, if present, the user can begin by creating a mating cable. #10 AWG is recommended for cable routing within the chassis, such as to a manipulator control board. #8 AWG is recommended for cable routing outside the chassis, noting that #8 AWG is acceptable in an exposed cable for 40 A, per UL 1740. The mating cable will connect to the yellow SB50 connector in left-rear of the chassis, under the top plate.
Always observe local laws and electrical standards valid to your region when building cables.
When building cables, be sure to consult the manufacturer documentation for full details on proper crimping.
| Description | Vendor Part | CPR Part Number |
|---|---|---|
| Mating connector | Anderson 992G5-BK | 022554 |
| Crimps, #8 AWG | Anderson 5952-BK | 017281 |
| Crimps, #10-12 AWG | Anderson 5953-BK | 022562 |
| Crimping tool | Anderson 1309G4 | N/A |
Replacing the Fuse
If you need to replace the fuse, use a Littlefuse F6792-ND as the replacement.
On/Off Control via Software
The High Power Expansion Kit output is controlled through software by publishing to the ROS topic /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_high_power,
similar to Software Control of User Power Rails.
The High Power Expansion Kit output is always disabled when the system powers up. The user must enable the output, via the ROS topic above, each time after the system powers up.
AUX Inputs
The Main circuit board provides 3 auxilliary inputs (AUX1 IN, AUX2 IN, AUX3 IN) that allow external payloads to provide inputs to the robot. Each of the three auxilliary inputs can be driven by one of the following:
- a 12 V input
- a 24 V input
- a push button or switch
In turn, the state of the input can be read from the ROS topic /a300_#####/platform/mcu/status/aux_inputs.
The AUX inputs are active low and are mapped to the ROS message bits as follows:
- AUX1 IN: bit 0
- AUX2 IN: bit 1
- AUX3 IN: bit 2
| AUX Input | Payload State | /a300_#####/platform/mcu/status/aux_inputs Value |
|---|---|---|
| AUX1 IN | 24 V on OR 12 V on OR button pressed 24 V off AND 12 V off AND button not pressed | bit 0 reads as '0' bit 0 reads as '1' |
| AUX2 IN | 24 V on OR 12 V on OR button pressed 24 V off AND 12 V off AND button not pressed | bit 1 reads as '0' bit 1 reads as '1' |
| AUX3 IN | 24 V on OR 12 V on OR button pressed 24 V off AND 12 V off AND button not pressed | bit 2 reads as '0' bit 2 reads as '1' |
AUX Input Pin Mapping
The pinout for each of the three connectors (AUX1 IN, AUX2 IN, AUX3 IN) is illustrated below.
| AUX IN connector pin | Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | 24 V In |
| 2 | 12 V In |
| 3 | Button/Switch In (3.3 V) |
| 4 | 24 V Return |
| 5 | 12 V Return |
| 6 | GND |
AUX Input Example #1
Consider the example where AUX2 IN has a 12 V supply connected to pins 2 and 5, with the remaining pins unconnected.
Monitor the input reading in ROS.
ros2 topic echo /a300_#####/platform/mcu/status/aux_inputs
| Action | /a300_#####/platform/mcu/status/aux_inputs value | Bit 2 Explanation | Bit 1 Explanation | Bit 0 Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Begin with the 12 V supply turned off | 7 (8b00000111) | '1' since AUX3 IN is not connected | '1' since 12 V supply is off | '1' since AUX1 IN is not connected |
| Turn the 12 V power supply on | 5 (8b00000101) | '1' since AUX3 IN is not connected | '0' since 12 V supply is on | '1' since AUX1 IN is not connected |
| Turn the 12 V supply off | 7 (8b00000111) | '1' since AUX3 IN is not connected | '1' since 12 V supply is off | '1' since AUX1 IN is not connected |
AUX Input Example #2
Consider the example where AUX1 IN has a 24 V supply connected to pins 1 and 4, AUX2 IN has a 12 V supply connected to pins 2 and 5, and AUX3 IN has a push button connected to pin 3.
| Action | /a300_#####/platform/mcu/status/aux_inputs value | Bit 2 Explanation | Bit 1 Explanation | Bit 0 Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Begin with 12 V supply turned off, the 24 V supply off, and the button not pressed | 7 (8b00000111) | '1' since button is not pressed | '1' since 12 V supply is off | '1' since 24 V supply is off |
| Turn the 24 V power supply on | 6 (8b00000110) | '1' since button is not pressed | '1' since 12 V supply is off | '0' since 24 V supply is on |
| Turn the 12 V supply on | 4 (8b00000100) | '1' since button is not pressed | '0' since 12 V supply is on | '0' 24 V supply is on |
| Press and hold the button | 0 (8b00000000) | '0' since button is pressed | '0' since 12 V supply is on | '0' 24 V supply is on |
AUX Outputs
The Main circuit board includes three user-controlled outputs (AUX1 OUT, AUX2 OUT, AUX3 OUT)
that can be controlled by publishing to the /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_aux_outputs ROS topic.
To enable the AUX outputs, simply
publish a single message with the appropriate bits set to 1 to turn the output on and 0 to turn
it off. The state does not persist so new commands will need to keep the bit enabled as well.
The AUX outputs are mapped to the ROS message bits as follows:
- AUX1 OUT: bit 0
- AUX2 OUT: bit 1
- AUX3 OUT: bit 2
Aux Output Examples
To disable all AUX outputs:
rostopic pub /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_aux_outputs std_msgs/UInt8 "data: 0"
To enable all AUX outputs:
rostopic pub /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_aux_outputs std_msgs/UInt8 "data: 7"
To enable just the AUX3 output:
rostopic pub /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_aux_outputs std_msgs/UInt8 "data: 4"
Aux Output Pin Mapping
Each of the AUX outputs is an 8-pin connector with pin mapping as outlined below. The output value is available in several modes:
- MOSFET outputs (x2)
- Normally open relay
- Normally closed relay
| AUX OUT connector pin | Function | Output when corresponding cmd_aux_outputs bit is '0' | Output when corresponding cmd_aux_outputs bit is '1' |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (AUX_24V) | 24 V output, fused at 3 A, available for use with relay | 24 V | 24 V |
| 2 (GND) | GND | GND | GND |
| 3 (AUX_RELAY_NC) | Normally closed relay pin | Connected to AUX_RELAY_COMMON | Floating |
| 4 (AUX_MOSFET2) | MOSFET #2 DRAIN | GND | Floating |
| 5 (GND) | GND | GND | GND |
| 6 (AUX_RELAY_COMMON) | Input that gets connected to AUX_RELAY_NC or AUX_RELAY_NO | Connected to AUX_RELAY_NC | Connected to AUX_RELAY_NO |
| 7 (AUX_RELAY_NO) | Normally open relay pin | Floating | Connected to AUX_RELAY_COMMON |
| 8 (AUX_MOSFET1) | MOSFET #1 DRAIN | GND | Floating |
General Purpose Inputs and Outputs (GPIO)
The Main circuit board includes four general purpose inputs and four general purpose
outputs, which are all connected to the 16-pin GPIO connector. All GPIOs are at the
3.3 V logic level. General purpose inputs are readable from the
/a300_#####/platform/mcu/status/gp_inputs ROS topic.
Publishing to the ROS /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_gp_outputs topic controls the general purpose outputs.
General Purpose Input Pin Mapping
| GPIO connector pin | Function | gp_inputs value when driven at 0 V | gp_inputs value when driven at 3.3 V |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | GP In 1 | Bit 0 is '0' | Bit 0 is '1' |
| 6 | GP In 2 | Bit 1 is '0' | Bit 1 is '1' |
| 7 | GP In 3 | Bit 2 is '0' | Bit 2 is '1' |
| 8 | GP In 4 | Bit 3 is '0' | Bit 3 is '1' |
| 13 | GND | N/A | N/A |
| 14 | GND | N/A | N/A |
| 15 | GND | N/A | N/A |
| 16 | GND | N/A | N/A |
General Purpose Output Pin Mapping
| GPIO connector pin | Function | Corresponding bit in cmd_gp_outputs | Output value when set to '0' | Output value when set to '1' |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GP Out 1 | 0 | 0 V | 3.3 V |
| 2 | GP Out 2 | 1 | 0 V | 3.3 V |
| 3 | GP Out 3 | 2 | 0 V | 3.3 V |
| 4 | GP Out 4 | 3 | 0 V | 3.3 V |
| 9 | GND | N/A | GND | GND |
| 10 | GND | N/A | GND | GND |
| 11 | GND | N/A | GND | GND |
| 12 | GND | N/A | GND | GND |
Fan Expansion
The Main circuit board has support for four additional 12 V brushless 4-wire PWM fans, one fan at each of FAN 5, FAN 6, FAN 7, and FAN 8. (FAN 1, FAN 2, FAN 3, and FAN 4 are reserved for internal use.) Examples of supported fans include CFM-8025BG-170-517-22 and 9GA0812P4J001.
The pinout for each fan is:
| Pin | Function / Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 12 V |
| 2 | GND |
| 3 | Tachometer (output from fan) |
| 4 | PWM (input to fan, 3.3 V) |
The speed of each fan can be controlled by publishing to the /a300_#####/platform/mcu/cmd_fans topic in ROS.
The speed of each fan can be monitored by reading the /a300_#####/platform/mcu/status/fans topic in ROS.
In both cases, the fan value is in the range from 0 (not spinning) to 255 (max speed).
Fans require spool up time on startup. Setting a fan to a very low value may result in the fan not rotating. The user must experiment with the values to find the corresponding minimum speed at which the fan can be started and operated.
Wireless Emergency Stop
A wireless dual-channel emergency stop can be added to Husky so that the emergency stop can be invoked remotely (either through a button press or when the remote unit is out of range), in addition to the two built-in Emergency Stop Buttons. Refer to the User Manual for details on how the Wireless Emergency Stop can be bypassed in certain debugging scenarios.
The Wireless Emergency Stop can be connected to Husky on the Main circuit board at the "W ES" connector, based on the pinout below.
| W ES Pin | Function / Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 24 V (fused at 3 A) |
| 2 | CAN High: combined with CAN Low, connected to the CAN2 pins on the MCU; see additional notes below |
| 3 | Reset In: Pull to GND for at least 100 ms to restart the robot after all emergency stops have been cleared; equivalent to pressing the Restart Button on Husky |
| 4 | Channel 1 Out (24 V): normally connected to Channel 1 In; disconnect to trigger an emergency stop |
| 5 | Channel 1 In |
| 6 | GND |
| 7 | CAN Low |
| 8 | GND |
| 9 | Channel 2 Out (24 V): normally connected to Channel 2 In; disconnect to trigger an emergency stop |
| 10 | Channel 2 In |
CAN Bus Connection
The CAN High and CAN Low pins are connected to the CAN2 bus of the system, shared with the battery and wireless charger subsystems.
The CAN2 bus is accessible on the computer as a linux socket under can1 at a bitrate of 250000.
Receiver Installation
In addition to the electrical integration noted above, the wireless receiver will normally require mechanical mounting inside the Husky, along with external mounting of an antenna. Refer to Wireless Stop receivers and Cable Passthrough for additional details.
External Emergency Stop
In addition to the two built-in Emergency Stop Button and in addition to the optional Wireless Emergency Stop, six additional emergency stop inputs are available on the Main circuit board (ES3 - ES8). By default, each of these are wired with a bypass connector. However, it is possible to remove a bypass connector and replace it with a connection to a device such as:
- Emergency Stop buttons
- Wireless Stop receivers
- Relays or similar PLC components
- Manipulator control cabinets
The pinout for ES3 - ES8 is shown below.
| ESx Pin | Function / Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | Channel 1 Out (24 V): normally connected to Channel 1 In; disconnect to trigger an emergency stop |
| 2 | Channel 1 In |
| 3 | Channel 2 Out (24 V): normally connected to Channel 2 In; disconnect to trigger an emergency stop |
| 4 | Channel 2 In |
Computer Power
Three connectors are provided for powering computers, including GPUs: SYS1, SYS2, and SYS3. Collectively, they provide up to 400 W of power at 12 V.
SYS1 / SYS2 Pinouts
| Pin | Function / Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 12 V |
| 2 | 12 V |
| 3 | GND |
| 4 | GND |
SYS3 Pinouts
| Pin | Function / Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 12 V |
| 2 | 12 V |
| 3 | 12 V |
| 4 | GND |
| 5 | GND |
| 6 | GND |
Other System Power
SYS4 is used to power the internal network switch and provides up to 60 W of power at 12 V.
SYS4 Pinouts
| Pin | Function / Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 12 V |
| 2 | GND |
Debug LEDs
A number of Debug LEDs are available for helping to debug system status. Their function is outlined below.
Common Core Debug LEDs
- D6: USB 5V: Solid green if a USB cable is plugged in and used to power the board
- D7: 3.3V: Solid green when the 3.3 V power rail is operational; else off
- D9: DBG/CON: For future use
- D11: HB/ERR: Heartbeat that toggles (red/off) every 500 ms when the main firmware loop is running; solid on or off indicates an error
DC/DC Debug LEDs
- D3: V OUT: Solid green when the output is operational; else off
Motor Controller LEDs
- 5V0: Solid green when the 5 V power rail is operational; else off
- 3V3: Solid green when the 3.3 V power rail is operational; else off
- MTR_FAULT: Solid red when a motor fault is detected; else off
- ERROR: Toggles (red/off) every 500 ms when a motor control error is detected; else off
- DBG2: For future use
- DBG1: Heartbeat that toggles (green/off) every 500 ms when the firmware loop is running; solid on or off indicates an error
Main Circuit Board Debug LEDs
- D2: UVB FLT: User power VBAT fault: red if the user battery rail is not enabled or if there has been a fault such as an overcurrent or over temperature event; else off
- D3: U24 FLT: User power 24V fault: red if the user 24V rail is not enabled or if there has been a fault such as an overcurrent or over temperature event; else off
- D4: U12A FLT: User power 12VA fault: red if the user 12VA rail is not enabled or if there has been a fault such as an overcurrent or over temperature event; else off
- D5: U12B FLT: User power 12VB fault: red if the user 12VB rail is not enabled or if there has been a fault such as an overcurrent or over temperature event; else off
- D6: PWR GD: Main power good indicator: red if any power supply is not enabled or has a fault; else off
- D7: 3.3V: Solid green if 3.3V rail is operational; else off
- D9: UPWR GD: User power good indicator: red if any of the 4 user power rails are not enabled or have a fault (including and overcurrent on any channel); else off
- D10: 5V: Solid green if 5V rail is operational; else off
- D12: APWR GD: Auxiliary power good indicator: red if either of the auxiliary power supplies are not enabled or has a fault (Auxiliary power supplies the USER power as well as other PCBA subsystem power rails at 12V and 24V); else off
- D13: SPWR GD: System power good indicator: red if either of the system power supplies are not enabled or has a fault (System power supplies the power for PCs, any optional GPU, and the primary network switch); else off
- D30: WES BP: Wireless E-Stop Bypass indicator: green if the Wireless E-Stop Bypass is enabled; else off
- D31: WES PFLT: Wireless E-Stop Power fault: red if the power supply is not enabled or has a fault; else off
- D46: XPWR GD: Expansion power good indicator: red if expansion power is not enabled or has a fault; else off
Software Integration
ROS has a large ecosystem of sensor drivers, some of which include pre-made URDF descriptions and even simulation configurations. Refer to Sensors supported by ROS.
For the best experience, consider purchasing supported accessories from Clearpath Robotics for your robot, which will include simulation, visualization, and driver support.
Refer to the following for more details:
Support
Clearpath is committed to your success. Please get in touch with us and we will do our best to get you rolling again quickly: <support@clearpathrobotics.com>.
To get in touch with a salesperson regarding Clearpath Robotics products, please email <research-sales@clearpathrobotics.com>.
If you have an issue that is specifically about ROS and is something which may be of interest to the broader community, consider asking it on Robotics Stack Exchange. If you do not get a satisfactory response, please ping us and include a link to your question as posted there. If appropriate, we will answer on Robotics Stack Exchange for the benefit of the community.