Navigation
Features
The OutdoorNav Software contains a set of features that can be enabled
or disabled according to your required application requirements. These
features can be enabled or disabled through the use of environment
variables, which should be added to the
/home/administrator/cpr_outdoornav_launch/outdoornav_tuning.env. The
following table describes the available features, their default state
and any additional parameters that we expose that may also be included
to tune the feature.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | The data collection feature enabled the user to record rosbag data of the sensors, localization, and navigation components of OutdoorNav. If true, rosbags will be saved and timestamed in the /home/administrator/onav_log/rosbag_data/ directory. If false, no rosbag will be recorded.Environment Variable: ENABLE_BAGGING (Default: false). |
| Collision Avoidance | Collision avoidance is the UGV's ability to detect obstacles and stop/maneuver around the obstacle without any collisions. If true, the UGV will detect obstacles and if false no obstacles will be detected. Setting to false is not recommended and may cause harm to property or to individuals.Environment Variable: ENABLE_COLLISION_AVOIDANCE (Default: true). |
| Obstacle Avoidance Mode | When collision avoidance is enabled, the UGV will behave in one of two ways according to the obstacle avoidance mode. If set to true, the UGV will perform obstacle avoidance maneuvers, replanning around detected obstacles. If set to false, the UGV will slow down to a stop in front of detected obstacles and wait for the obstacle to clear before proceeding.Environment Variable: OBSTACLE_AVOIDANCE_MODE (Default: true). |
| Continuous Planning | The continuous planning feature allows the UGV to continuously monitor whether an obstacle is on the UGV's path and replan around said obstacle smoothly without the need for stopping in front of the obstacle. If disabled, the UGV will come to a full stop in front of an obstacle and then replan around said obstacle. Environment Variable: ENABLE_CONTINUOUS_PLANNER (Default: true). |
| Path Smoothing | The path smoothing feature according to a specified turning radius. The default behaviour will generate point-to-point straight line paths. Environment Variable: ENABLE_PATH_SMOOTHER (Default: false). |
| Path Shifting | The path shifting feature is designed to reduce the oscillation around the initial reference path if the UGV begins to deviate of said reference path. It is particularly useful for the Clearpath Robotics Warthog platform whose tires are incredibly pliable and results in unmodelled effects on the navigation. Environment Variable: ENABLE_PATH_SHIFTING (Default: false). |
| Constrained Replanning | The constrained replanning feature restricts the area in which replanning paths can be generated. For example, if a REPLANNING_CONSTRAINT of 3.0 m is used, the UGV will not be allowed to replan a path that drives it more than 3.0 m from the initial path. This replanning area can be shown on the map over the connecting lines between waypoints. See Constrained Replanning for further details.Environment Variable: ENABLE_CONSTRAINED_REPLANNING (Default: false).Use the REPLANNING_CONSTRAINT environment variable to modify the replanning constraint (in meters). |
| Stop Distance | The stop distance feature allows the UGV to stop a predefined distance away from obstacles. This is useful if a UGV cannot drive in reverse and needs the required room in front of it to replan around an obstacle. Environment Variable: ENABLE_STOP_DISTANCE (Default: false)Use the STOP_DISTANCE environment variable to modify the stop distance (in meters). Note that if the stop distance is larger than 4.5 meters for the Clearpath Robotics Jackal and Husky UGVs, or 10.0 meters for the Clearpath Robotics Warthog UGV, the computational load will increase and may cause a decrease in performance in the navigation. |
| Delay Compensation | The delay compensation feature is able to compensate for mechanical delay on UGVs where either the accelerator introduces delay into the linear velocity or the steering introduces delay in the angular velocity. This feature is not required for Clearpath Robotics UGVs as negligible delay is present in our system. Environment Variable: ENABLE_DELAY_COMPENSATION (Default: false)Use the CONTROLLER_DELAY environment variable to modify the amount of delay to be compensated (in milliseconds). |
Advanced Configuration
The following section provides a list of environment variables that can
be modified in order to tune both the sensor systems as well as tuning
the navigation software. All of the environment variables listed below
can be modified in the
/home/administrator/cpr_outdoornav_launch/outdoornav_tuning.env file.
Sensor Tuning
The following table lists the sensors that are useable with the OutdoorNav software. These sensor drivers can be turned on/off using these environment variables, however, the sensor will always remain powered on.
| Environment Variable | Description | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| SWIFTNAV_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disable the Swiftnav Piksi/Duro ROS driver, if integrated. | bool |
| UBLOX_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disable the UBlox ROS driver, if integrated. | bool |
| MICROSTRAIN_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disable the Microstrain GX5/CV5 ROS driver, if integrated. | bool |
| XSENS_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disable the XSens MTI ROS driver, if integrated. | bool |
| VLP_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disable the Velodyne ROS driver, if integrated (front unit if more than one). | bool |
| REAR_VLP_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disable the Velodyne ROS driver, if integrated (rear unit if more than one). | bool |
| LMS1XX_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disbale the Sick LMS1XX ROS driver, if integrated (front unit if more than one). | bool |
| REAR_LMS1XX_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disbale the Sick LMS1XX ROS driver, if integrated (rear unit if more than one). | bool |
| HOKUYO_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disbale the Hokuyo ROS driver, if integrated (front unit if more than one). | bool |
| REAR_HOKUYO_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disbale the Hokuyo ROS driver, if integrated (rear unit if more than one). | bool |
| D435_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disable the Realsense ROS driver, if integrated (front unit if more than one). | bool |
| REAR_D435_ENABLE_DRIVER | Enable/disable the Realsense ROS driver, if integrated (rear unit if more than one). | bool |
Sensor Tuning (Advanced)
The following list of environment variables can be used to filter the sensor data in order to modify/improve the sensory input to the OutdoorNav autonomy. It is recommended that you first consult the following links before attempting to modify these parameters.
Voxel Grid Filter
| Environment Variable | Description | Data Type (Default) |
|---|---|---|
| <type>_ENABLE_FILTER_VOXEL | Enable/disable the PCL voxel filter for the sensor of type <type>. type = {VLP, D435, REAR_VLP, REAR_D435} | bool (false) |
| PCL_FIL_FILTER_VOXEL_LEAF_SIZE | The size of a leaf (on x,y,z), in meters, used for downsampling. Range: 0.0 to 1.0. | double (0.01) |
Cropbox Filter
| Environment Variable | Description | Data Type (Default) |
|---|---|---|
| <type>_ENABLE_FILTER_CROPBOX | Enable/disable the PCL cropbox filter for the sensor of type <type>. type = {VLP, D435, REAR_VLP, REAR_D435} | bool (false) |
| PCL_FILTER_CROPBOX_MIN_X | The lower bound, in meters, on the x-axis within which to reject points from the pointcloud. Range: -1000.0 to 1000.0. | double (0.01) |
| PCL_FILTER_CROPBOX_MAX_X | The upper bound, in meters, on the x-axis within which to reject points from the pointcloud. Range: -1000.0 to 1000.0. | double (2.0) |
| PCL_FILTER_CROPBOX_MIN_Y | The lower bound, in meters, on the y-axis within which to reject points from the pointcloud. Range: -1000.0 to 1000.0. | double (-10.0) |
| PCL_FILTER_CROPBOX_MAX_Y | The upper bound, in meters, on the y-axis within which to reject points from the pointcloud. Range: -1000.0 to 1000.0. | double (10.0) |
| PCL_FILTER_CROPBOX_MIN_Z | The lower bound, in meters, on the z-axis within which to reject points from the pointcloud. Range: -1000.0 to 1000.0. | double (-0.5) |
| PCL_FILTER_CROPBOX_MAX_Z | The upper bound, in meters, on the z-axis within which to reject points from the pointcloud. Range: -1000.0 to 1000.0. | double (10.0) |
Radius Outlier Filter
| Environment Variable | Description | Data Type (Default) |
|---|---|---|
| <type>_ENABLE_FILTER_RADIUS_OUTLIER | Enable/disable the PCL radius outlier filter for the sensor of type <type>. type = {VLP, D435, REAR_VLP, REAR_D435} | bool (false) |
| PCL_FILTER_ROR_RADIUS_SEARCH | The number of points within this distance, in meters, from the query point will need to be equal or greater than PCL_FILTER_ROR_MIN_NEIGHBORS in order to be classified as an inlier point (i.e. will not be filtered). | double (0.05) |
| PCL_FILTER_ROR_MIN_NEIGHBORS | The number of points within PCL_FILTER_ROR_RADIUS_SEARCH from the query point will need to be equal or greater than this number in order to be classified as an inlier point (i.e. will not be filtered). | int (10) |
Statistical Outlier Filter
| Environment Variable | Description | Data Type (Default) |
|---|---|---|
| <type>_ENABLE_FILTER_STATISTICAL_OUTLIER | Enable/disable the PCL statistical outlier filter for the sensor of type <type>. type = {VLP, D435, REAR_VLP, REAR_D435} | bool (false) |
| PCL_FILTER_SOR_MEAN_K | The number of points (k) to use for mean distance estimation Range: 2 to 100. | double (5.0) |
| PCL_FILTER_SOR_STD_DEV | The standard deviation multiplier threshold. All points outside the mean +- sigma * std_mul will be considered outliers. Range: 0.0 to 5.0. | double (0.3) |
PointCloud to LaserScan Filter
| Environment Variable | Description | Data Type (Default) |
|---|---|---|
| <type>_ENABLE_POINTCLOUD_TO_LASERSCAN | Enable/disable the pointcloud to laserscan outlier filter for the sensor of type <type>. type = {VLP, D435, REAR_VLP, REAR_D435} | bool (false) |
| PCL_TO_SCAN_MIN_HEIGHT | The minimum height to sample in the point cloud, in meters. | double (0.2) |
| PCL_TO_SCAN_MAX_HEIGHT | The maximum height to sample in the point cloud, in meters. | double (1.2) |
| PCL_TO_SCAN_MIN_ANGLE | The minimum scan angle, in radians. | double (3.14) |
| PCL_TO_SCAN_MAX_ANGLE | The maximum scan angle, in radians. | double (3.14) |
| PCL_TO_SCAN_ANGLE_INCREMENT | Resolution of laser scan, in radians, per ray. | double (0.00218) |
| PCL_TO_SCAN_TIME | The scan rate in seconds. | double (0.3333) |
| PCL_TO_SCAN_MIN_RANGE | The minimum ranges to return, in meters. | double (0.3) |
| PCL_TO_SCAN_MAX_RANGE | The maximum ranges to return, in meters. | double (100.0) |
DepthImage to LaserScan Filter
| Environment Variable | Description | Data Type (Default) |
|---|---|---|
| <type>_ENABLE_DEPTH_TO_LASERSCAN | Enable/disable the depth image to laserscan outlier filter for the sensor of type <type>. type = {D435, REAR_D435} | bool (false) |
| DEPTH_TO_SCAN_HEIGHT | The number of pixel rows to use to generate the laserscan. For each column, the scan will return the minimum value for those pixels centered vertically in the image. | int |
| DEPTH_TO_SCAN_TIME | Time between scans (seconds). Typically, 1.0/frame_rate. This value is not easily calculated from consecutive messages, and is thus left to the user to set correctly. | double |
| DEPTH_TO_SCAN_MIN_RANGE | The minimum ranges to return in meters. Ranges less than this will be output as -Inf. | double |
| DEPTH_TO_SCAN_MAX_RANGE | The maximum ranges to return in meters. Ranges greater than this will be output as +Inf. | double |
Navigation Tuning
The following table lists the environment variables that can be used to enable/disable which sensor is used as part of the collision avoidance feature of OutdoorNav.
| Environment Variable | Description | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| VLP_ENABLE_COSTMAP | Enable/disable the Velodyne from populating the costmap and being used for collision avoidance. This variable should only be used if the sensor is integrated (front unit if more than one). | bool |
| REAR_VLP_ENABLE_COSTMAP | Enable/disable the Velodyne from populating the costmap and being used for collision avoidance. This variable should only be used if the sensor is integrated (rear unit if more than one). | bool |
| LMS1XX_ENABLE_COSTMAP | Enable/disable the Sick LMS1XX from populating the costmap and being used for collision avoidance. This variable should only be used if the sensor is integrated (front unit if more than one). | bool |
| REAR_LMS1XX_ENABLE_COSTMAP | Enable/disable the Sick LMS1XX from populating the costmap and being used for collision avoidance. This variable should only be used if the sensor is integrated (rear unit if more than one). | bool |
| HOKUYO_ENABLE_COSTMAP | Enable/disable the Hokuyo from populating the costmap and being used for collision avoidance. This variable should only be used if the sensor is integrated (front unit if more than one). | bool |
| REAR_HOKUYO_ENABLE_COSTMAP | Enable/disable the Hokuyo from populating the costmap and being used for collision avoidance. This variable should only be used if the sensor is integrated (rear unit if more than one). | bool |
| D435_ENABLE_COSTMAP | Enable/disable the Realsense from populating the costmap and being used for collision avoidance. This variable should only be used if the sensor is integrated (front unit if more than one). | bool |
| REAR_D435_ENABLE_COSTMAP | Enable/disable the Realsense from populating the costmap and being used for collision avoidance. This variable should only be used if the sensor is integrated (rear unit if more than one). | bool |
Navigation Tuning (Advanced)
The following list of environment variables can be used to modify some of the navigation inputs of to the OutdoorNav autonomy. It is recommended that you first consult the following link(s) before attempting to modify these parameters.
| Environment Variable | Description | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| COSTMAP_LIDAR_<2D/3D>_OBSTACLE_RANGE | The maximum range in meters at which to insert obstacles into the costmap using sensor data. This can apply for either 2D or 3D variables, associated with 2D and 3D lidars, respectively (front unit if more than one). | double |
| COSTMAP_LIDAR_<2D/3D>_RAYTRACE_RANGE | The maximum range in meters at which to raytrace out obstacles from the map using sensor data. This can apply for either 2D or 3D variables, associated with 2D and 3D lidars, respectively (front unit if more than one). | double |
| COSTMAP_REAR_LIDAR_<2D/3D>_OBSTACLE_RANGE | The maximum range in meters at which to insert obstacles into the costmap using sensor data. This can apply for either 2D or 3D variables, associated with 2D and 3D lidars, respectively (rear unit if more than one). | double |
| COSTMAP_REAR_LIDAR_<2D/3D>_RAYTRACE_RANGE | The maximum range in meters at which to raytrace out obstacles from the map using sensor data. This can apply for either 2D or 3D variables, associated with 2D and 3D lidars, respectively (front unit if more than one). | double |
Command Line Operation
By default the OutdoorNav Software, including the Navigation component, begins automatically when the system is powered on. This section outlines the commands that can be used by developers who are debugging the system or who want more precise control for managing the Navigation component.
Connecting to the OutdoorNav Computer
To connect to your UGV, consult its corresponding user manual.
If you are using a Clearpath Robotics UGV with an OutdoorNav computer,
first ssh to the UGV using the details provided in the UGV user
manual. If you have a wired connection to the Clearpath Robotics UGV,
use the following command. If using wifi, you can replace the IP address
with the wifi-assigned IP address or the hostname of the UGV.
ssh administrator@192.168.131.1
Then, connect to the OutdoorNav Computer:
ssh administrator@192.168.131.100
Starting the Navigation Software
Begin by connecting to the OutdoorNav Computer as outlined above.
On UGV startup, all the sensors, the user interface, as well as the
Navigation software are set to start automatically through a Docker
container. You can check the Docker container's status by running
docker compose ps and checking for:
- onav-web (Docker image containing the web interface)
- onav-web-ros (Docker image containing the ROS web bridge nodes)
- onav-sensors (Docker image containing that launches the ROS sensor drivers)
- onav-autonomy (Docker image containing the ROS nodes related to the autonomy)
If the Docker containers are not running, they can be started with:
cd ~/cpr_outdoornav_launch/ # directory with docker-compose.yaml
docker compose --profile outdoornav up -d
Stopping/Restarting all of OutdoorNav
To use the UGV without the OutdoorNav software, use these commands to stop the software and prevent it from automatic startup:
cd ~/cpr_outdoornav_launch/ # directory with docker-compose.yaml
docker compose --profile outdoornav stop
If the OutdoorNav software is currently running or has been stopped, it can be restarted by running:
cd ~/cpr_outdoornav_launch/ # directory with docker-compose.yaml
docker compose --profile outdoornav start
Stopping/Restarting the Autonomy
To use the UGV without the autonomy core of OutdoorNav, use these commands to stop the nodes and prevent them from automatic startup:
cd ~/cpr_outdoornav_launch/ # directory with docker-compose.yaml
docker compose --profile autonomy stop
The autonomy core can be restarted by running:
cd ~/cpr_outdoornav_launch/ # directory with docker-compose.yaml
docker compose --profile outdoornav start
Stopping/Restarting the Sensors
To use the UGV without the sensors, use these commands to disable the nodes and prevent them from automatic startup:
cd ~/cpr_outdoornav_launch/ # directory with docker-compose.yaml
docker compose stop
Accessing the Shell in Docker Container
To access the shell in a Docker container for debugging (optionally
replace onav-autonomy with onav-web in the following command):
cd ~/cpr_outdoornav_launch/ # directory with docker-compose.yaml
docker compose exec -it onav-autonomy bash
Accessing the Navigation Software Logs
To check the logs of the Navigation software:
cd ~/cpr_outdoornav_launch/ # The directory with docker-compose.yaml
docker compose logs -f
Validating TF Setup
Sensor TF validation should only be required if the performance is noticeably poor, such as when the UGV drifts off of the planned path or oscillations occur around the path).
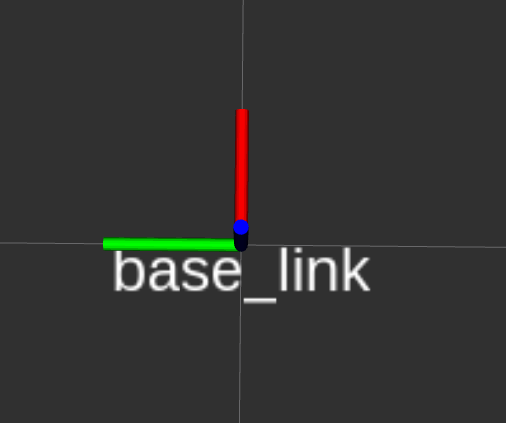
The coordinate transformation of the two GPS antennas, the IMU, the 2D and 3D Lidars to the base_link of the UGV should have already been set prior to receiving the UGV. However, ensure that they are set correctly.
The ROS coordinate frame base_link, shown in the figure below, is located at the center of the bottom plate of the UGV. The environment variables below should be taken with respect to this coordinate frame. The X axis is in red (and pointing towards the front of the UGV), Y in green (pointing towards the left of the UGV) and Z in blue (pointing towards the sky).
You can check the current value of the environment variables by running the following (and setting <variable_name> to the names listed in the table below).
printenv | grep <variable_name>
The environment variables for the position and orientation of each sensor are provided in the table below.
GPS Navigation sensor position and orientation environment variables
| Environment Variable | Function |
|---|---|
| POSITION_GPS_XYZ | [X,Y,Z] position, in meters, of the position (rear) GPS antenna with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
| POSITION_GPS_RPY | [Roll,Pitch,Yaw], in radians, of the position (rear) GPS antenna with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
| HEADING_GPS_XYZ | [X,Y,Z] position, in meters, of the heading (front) GPS antenna with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
| HEADING_GPS_RPY | [Roll,Pitch,Yaw], in radians, of the heading (front) GPS antenna with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
| MICROSTRAIN_XYZ | [X,Y,Z] position, in meters, of the IMU with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
| MICROSTRAIN_RPY | [Roll,Pitch,Yaw], in radians, of the IMU with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
| LIDAR_XYZ | [X,Y,Z] position, in meters, of the 3D Lidar with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
| LIDAR_RPY | [Roll,Pitch,Yaw], in radians, of the 3D Lidar with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
| LASER_XYZ | [X,Y,Z] position, in meters, of the 2D Lidar with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
| LASER_RPY | [Roll,Pitch,Yaw], in radians, of the 2D Lidar with respect to the base_link coordinate frame. |
When the printed Y axis on the IMU is pointing towards the front of the robot (i.e., aligned to X axis of base_link), MICROSTRAIN_RPY = [0, 0, 0].
If you decide to move any of these sensors, you must modify these variables accordingly.